Vitamin D deficiency linked to high BP
People with lower levels of vitamin D are more likely to have stiffer arteries and an inability of blood vessels to relax, according to a new study.
The findings by the scientists at the Emory/Georgia Tech Predictive Health Institute add to evidence that lack of vitamin D can lead to impaired vascular health, contributing to high blood pressure and the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Study participants who increased their vitamin D levels were able to improve vascular health and lower their blood pressure.
Ibhar Al Mheid, a cardiovascular researcher at the University conducted the study with Arshed Quyyumi, professor of medicine and director of the Emory Cardiovascular Research Institute.
The 554 participants in the study were Emory or Georgia Tech employees –average age 47 and generally healthy who are taking part in the Center for Health Discovery and Well Being, part of the Emory/Georgia Tech Predictive Health Institute.
The average level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (a stable form of the vitamin reflecting diet as well as production in the skin) in participants' blood was 31.8 nanograms per milliliter.
In this group, 14 per cent had 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels considered deficient, or less than 20 nanograms per milliliter, and 33 per cent had levels considered insufficient, less than 30 nanograms per milliliter.
The researchers monitored the ability of participants' blood vessels to relax by inflating and then removing a blood pressure cuff on their arms. To allow blood to flow back into the arm, blood vessels must relax and enlarge – a change that can be measured by ultrasound.
The researchers also made other measurements of smaller blood vessels and examined the resistance to blood flow imposed by the arteries.
"Even after controlling for factors such as age, weight and cholesterol, people with lower vitamin D levels still had stiffer arteries and impaired vascular function," said Al Mheid.
"We found that people with vitamin D deficiency had vascular dysfunction comparable to those with diabetes or hypertension," he said.
Participants whose vitamin D levels increased over the next six months, either from dietary supplements or ample sun exposure, tended to improve their measures of vascular health and had lower blood pressure.
Forty-two study participants with vitamin D insufficiency whose levels later went back to normal had an average drop in blood pressure of 4.6 millimeters mercury.
The study was presented at the annual American College of Cardiology meeting in New Orleans.
Vitamin D
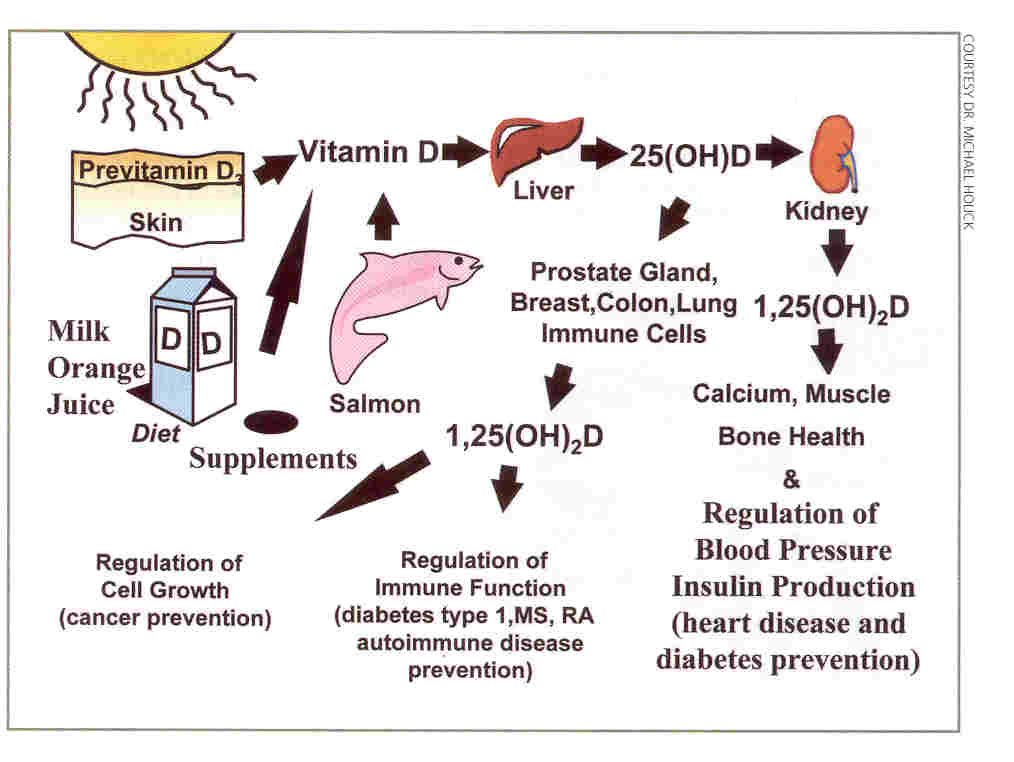
Vitamin D is found in many dietary sources such as fish, eggs, fortified milk, and cod liver oil. The sun also contributes significantly to the daily production of vitamin D, and as little as 10 minutes of exposure is thought to be enough to prevent deficiencies. The term “vitamin D” refers to several different forms of this vitamin.
Two forms of Vitamin D are important in humans: ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3). Vitamin D2 is synthesized by plants. Vitamin D3 is synthesized by humans in the skin when it is exposed to ultraviolet-B (UVB) rays from sunlight. Foods may be fortified with vitamin D2 or D3.
Vitamin D Needs and Deficiency
The major biologic function of vitamin D is to maintain normal blood levels of calcium and phosphorus. Vitamin D aids in the absorption of calcium, helping to form and maintain strong bones. Recently, research also suggests vitamin D may provide protection from osteoporosis, hypertension (high blood pressure), cancer, and several autoimmune diseases.
Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium, which your bones need to grow. A lack of vitamin D can lead to bone diseases such as osteoporosis or rickets. Vitamin D also has a role in your nerve, muscle, and immune systems.
Vitamin D is measured as Serum 25-Hydroxy vitamin D levels. A Serum Hydroxy vitamin D level of 10 ng/mL is low, a level of 15 ng/mL is adequate and a level of 200 ng/mL is potentially toxic
Rickets and osteomalacia are classic vitamin D deficiency diseases. In children, vitamin D deficiency causes rickets, which results in skeletal deformities. In adults, vitamin D deficiencycan lead to osteomalacia, which results in muscular weakness in addition to weak bones. Populations who may be at a high risk for vitamin D deficiencies include the elderly, obese individuals, exclusively breastfed infants, and those who have limited sun exposure. Also, individuals who have fat malabsorption syndromes (e.g., cystic fibrosis) or inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., Crohn’s disease) are at risk.
How to Get Vitamin D
You can get vitamin D in three ways: through your skin, from your diet, and from supplements. Your body forms Vitamin D naturally after exposure to sunlight. However, too much sun exposure can lead to skin aging and skin cancer. So many people try to get their vitamin D from other sources. You need to get anywhere between 200IU to 600IU of Vitamin D a day with the amount increasing as we age.
Vitamin D-rich foods include egg yolks, saltwater fish, and liver. Some other foods, like milk and cereal, often have added vitamin D.
You can also take vitamin D supplements. Check with your health care provider to see how much you should take. People who might need extra vitamin D include
- Seniors
- Breastfed infant
- People with dark skin
- People with certain conditions, such as liver diseases, cystic fibrosis and Crohn’s disease
- People who are obese or have had gastric bypass surgery
Foods high in Vitamin D
| Cod liver oil, 1 tablespoon | 1,360 |
| Salmon (sockeye), cooked, 3 ounces | 794 |
| Mackerel, cooked, 3 ounces | 388 |
| Tuna fish, canned in water, 3 ounces | 154 |
| Milk, nonfat, reduced fat, and whole | 115 |
| Orange juice fortified with vitamin D, 1 cup | 100 |
| Yogurt, fortified, 6 ounces | 80 |
| Margarine, fortified, 1 tablespoon | 60 |
| Sardines, canned in oil, drained, 2 sardines | 46 |
| Liver, beef, cooked, 3.5 ounces | 46 |
| Ready-to-eat cereal, fortified | 40 |
| Egg, 1 whole (vitamin D is found in yolk) | 25 |
| Cheese, Swiss, 1 ounce | 6 |
In a not very scientific survey I have personally found that many women are very deficient in Vitamin D. My wife and some of here friends have had to supplement a lot of Vitamin D just to try to catch up
once the bodys requirements have been met vit d, my wife needs vitamin d, at what vitamin d level do you start to syore the vitamin d, vitamin D fitness tips for life, vitamin d, treatment of vitamin d deficiency inuit d2, The sun contributes significantlyto the daily exposure, The sun also contributes significantly to the daily production of Vitamin D AND AS LITTLE AS 10 MINUTES OF EXPOSURE IS THOUGHT TO BE ENOUGH TO PREVENT deficiences -2009 August 26






No comments:
Post a Comment